In addition to the constituents of the hazardous material, the SDS identifies the hazards associated with it. Hazards are used to quantify how dangerous the substance is. The particular hazards associated with the material determine how it must be handled and stored and may have a bearing on treatment if a user is exposed.
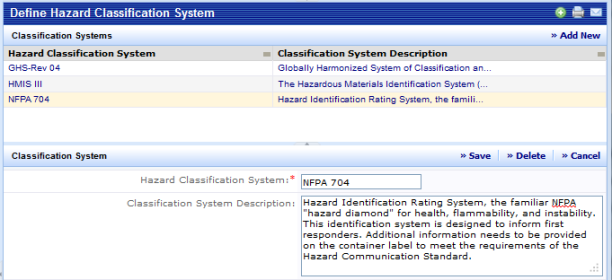
International governing agencies, national governing agencies, manufacturers, and other organizations all offer systems of classifying hazardous products. You will need to identify the hazard classification systems used at your facility. The SDS application ships with four classification systems:
GHS (Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals) was developed by the United Nations for providing consistent guidelines that all countries can use in classifying and labeling hazardous products.
67/548/EEC is the classification system of the Dangerous Substances Directive of the European Union.
If you choose to use these classification systems, make sure you review the definitions for consistency with the classification system specified for your site. As a courtesy, the tables composing the hazard classification system are already completed with a number of standard international classification systems.
The classifications used at your site may not be limited to a single system. For example some chemicals might require fire protection classification while others may require GHS classification. The systems used by your site are determined by the regulatory agencies and the management procedures that govern your operations. Moreover, a particular substance may be governed by multiple classifications.
Rather than lock users into a predefined set of classifications, the SDS application provides the ability for each site to define the hazard classification systems they require by using a variety of levels:
For example, HMIS (classification system) might be divided into the Health, Flammability, and Personal Protection classes. The Health class can then be divided into numeric categories.

When the view is first presented, it lists all classification systems. A Smart Search console in the grid allows you to filter or sort data on any of the displayed columns. See Restricting Data Using Smart Search.
| Field | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
Hazard Classification System |
(Required Field) The identifier for the classification system. This value must be unique. |
|
Classification System Description |
A free-form text description of the classification system. If this system is based on an industry standard system, you should include references to the source and version of the standard, such as its URL address. |
Note: ARCHIBUS performs a cascading delete, so when you delete a classification system, ARCHIBUS automatically deletes all associated classes and categories as well. You will not have the ability to "Undo" this delete, so make sure you really want to remove the whole hazard classification system.
Define the component classes and categories by using the following tasks in the Environmental & Risk Management / Hazardous Materials /Business Process Owner - Hazmat process:
When entering the hazard classification systems, you may want to consult these sources for information on common classification systems:
National Fire Protectors Association (NFPA) Codes and Standards: http://www.nfpa.org/aboutthecodes/list_of_codes_and_standards.asp
European Commission guide to the GHS: http://ec.europa.eu/enterprise/sectors/chemicals/classification/
| Copyright © 1984-2016, ARCHIBUS, Inc. All rights reserved. |